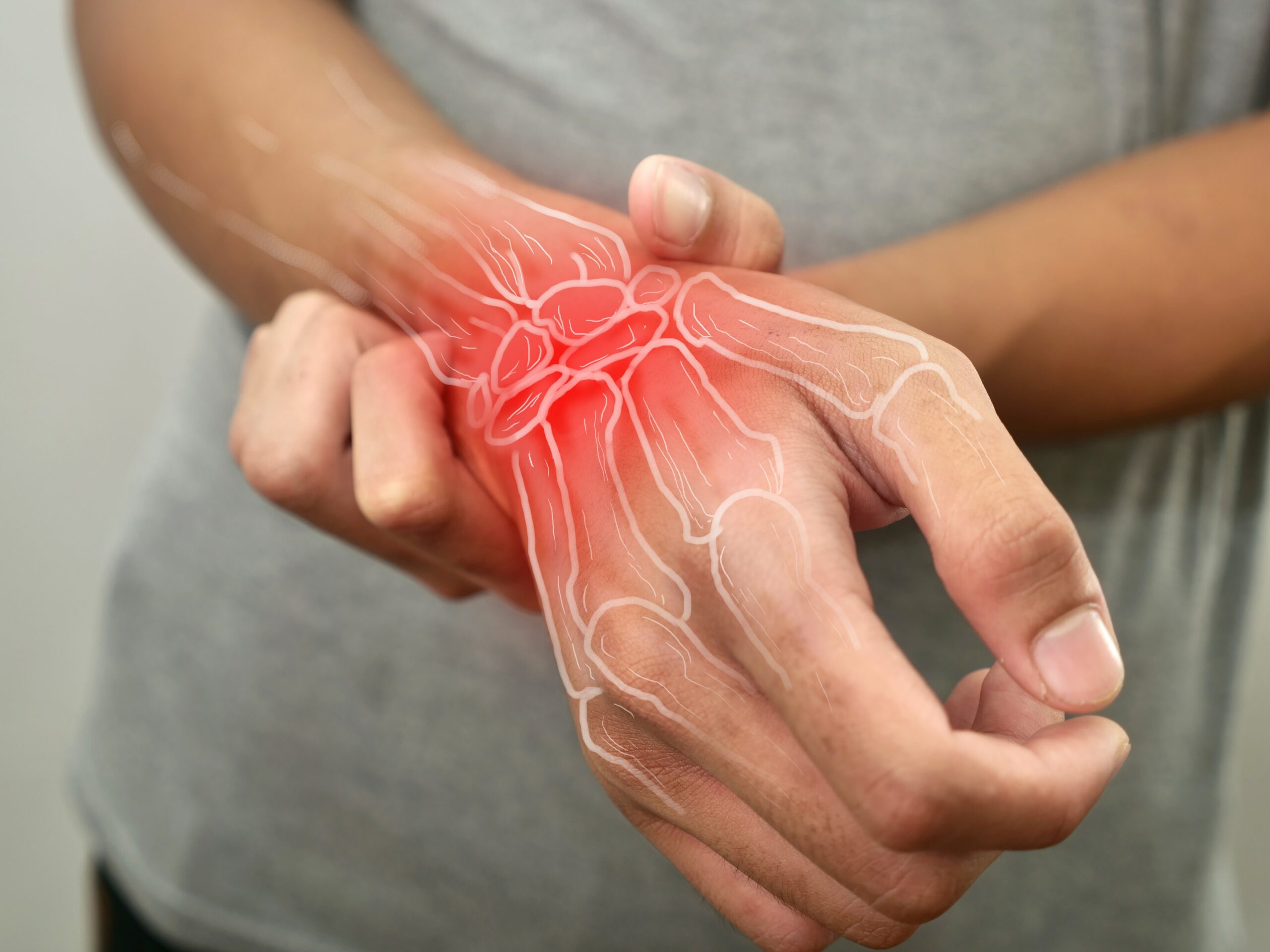
Because the wrist has a complex structure, it can be more exposed to pain, which is often ignored. Surgeon Ömer Yonga, M.D. Orthopedics and Traumatology states that wrist pain may occur for reasons other than trauma and emphasizes that these pains should be taken seriously.
Pain in the wrist, which plays a very important role in the ability of the hand to perform its movements, is one of the common joint problems. People who have to work in front of a computer for a long time, do sports or do a job that requires repetitive wrist movements are in the potential risk group for wrist pain. However, wrist pain may occur after some diseases, wrong exercises and trauma. Surgeon Ömer Yonga, M.D. Orthopedics and Traumatology at Koşuyolu Hospital, Yeditepe University, pointed out the importance of consulting a doctor in time at this point. Underlining that there may be more serious problems than what appears on the basis of the pain, Dr. Yonga said that neglecting pain, trying to self-diagnose and treat, continuing painful movements, overusing painkillers, forcing movements despite pain, and going to the doctor late are among the most common mistakes made by patients.
The complex structure of the wrist increases the potential for injury
“The anatomical structure of the wrist consists of a series of bones, ligaments, tendons and nerves. These structures ensure the durability of the wrist and allow various movements. However, this complexity can also increase the potential for vulnerability to injury,” said Medical Dr. Yonga said, “Wrist injuries can occur due to various factors such as falls, impacts, repetitive movements, fractures or sprains. Taking protective measures and paying attention to proper ergonomics can reduce wrist injuries. It is important to use protective equipment and perform repetitive movements carefully, especially during risky activities.”
These diseases cause pain in the wrist!
Noting that some diseases, independent of trauma, can also cause pain in the wrist, Medical Dr. Yonga Dr. Yonga explained the following on the subject, “The most common wrist disorders are inflammation of the tendons in the wrist (tendinitis-tenosynovitis), compression of the median nerve in the wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome), inflammation of the tendons on the side of the thumb (de quervain tenosynovitis), stretching or tearing ligaments in the wrist, formation of fluid-filled sacs in the tendon or joint capsule of the wrist (ganglion cysts), fracture or sprain of the wrist bones and accumulation of uric acid in the joints.”
 The character of the pain is an important clue
The character of the pain is an important clue
Stating that the character of wrist pain provides an important clue in determining the underlying problem, Dr. Yonga explained the following about these signs, “While sharp-sudden onset of pain may occur due to fracture, sprain, ligament injury or acute trauma, smooth and slow-onset pain may be due to chronic overuse tendinitis. The fact that the pain wakes the patient up at night, that the patient feels the need to shake his hands, and that he frequently starts to drop objects such as glasses and plates from his hands due to loss of strength, makes us think of carpal tunnel syndrome. Swelling accompanying pain may occur in ganglion or other soft tissue masses. These characteristics are important for a healthcare professional in the clinical evaluation and diagnosis process. In addition, details such as the onset of pain, its severity, frequency, and sensitivity to other factors should also be evaluated. It should not be forgotten that everyone’s perception of pain is different and the same type of pain may occur due to different reasons.”
Those with thin wrists should pay more attention!
Recording that whether a person’s wrist is thin or thick may pose a risk for problems that may occur in the wrist, Dr. Yonga said that a thin wrist generally has less soft tissue, which can lead to bones and other structures being more vulnerable to external factors. Tendons and ligaments may be more prominent in thin wrists, causing these structures to become more sensitive to external factors. When individuals with thin wrists are exposed to the same forces, this force may be felt more on the individual’s wrist, thus increasing the risk of injury. It should not be forgotten that wrist structure is not the sole determinant of wrist problems. A number of factors may also be influential, such as activity levels, age, general health, exercise habits and work conditions.
“Wrist pain can cause different problems if not taken seriously.”
Pointing out that wrist pain can be serious and can cause different problems if neglected, Op. Dr. Yonga explained the following on the subject, “For example, long-term compression of the nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome can cause permanent damage to the nerve. Again, if tendon inflammation is not treated, it can lead to long-term loss of function and tendon damage. Untreated or missed fractures and dislocations can cause pain, swelling, limitation of movement in the joint and joint damage in the future, and cysts, which we call ganglion, can put pressure on the nerves and tendons around them as they grow, which causes pain. Therefore, wrist pain should be taken seriously and the underlying cause should be revealed.” Surgeon Ömer Yonga, M.D. Orthopedics and Traumatology at Yeditepe University Hospitals warned as follows, “It is important to rest the painful wrist, avoid overuse and take appropriate protective measures. Paying attention to ergonomics in the work or home environment can also protect the wrist from excessive strain. In addition, in case of pain, an orthopedic specialist should be consulted without wasting time.”