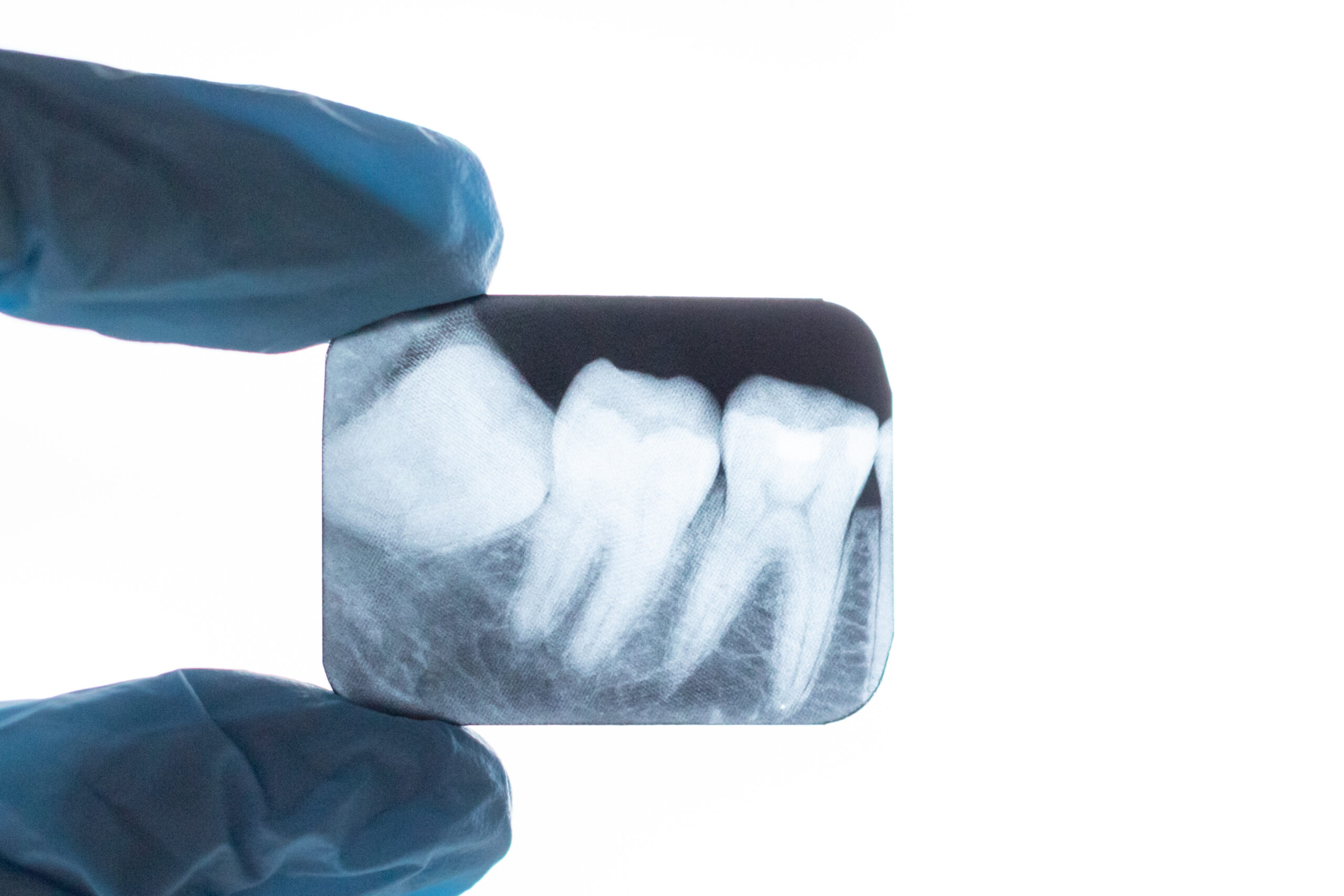
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Lect. Prof. Dr. Seda Altop, Üsküdar Dental Hospital made evaluations about whether wisdom teeth should be extracted or not. Altop stated that such teeth can form a sac around them even if they are asymptomatic, and each case needs a separate evaluation.
Experts state that there is no need to extract wisdom teeth that are fully erupted and in a suitable position. However, noting that problems such as gingivitis may occur in semi-impacted wisdom teeth, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Lect. Prof. Dr. Seda Altop, Üsküdar Dental Hospital said, “In this case, problems such as abscesses on the jaw face, swelling on the face, pain and limitation in mouth opening may occur and may need to be withdrawn.” said. Emphasizing the need for radiographic evaluation to determine whether there is a problem, Altop said that the decision to extract can be made after the evaluation of issues such as the anatomical relationship with the nerve, whether a cyst is formed, and damage to the surrounding tissue and teeth.
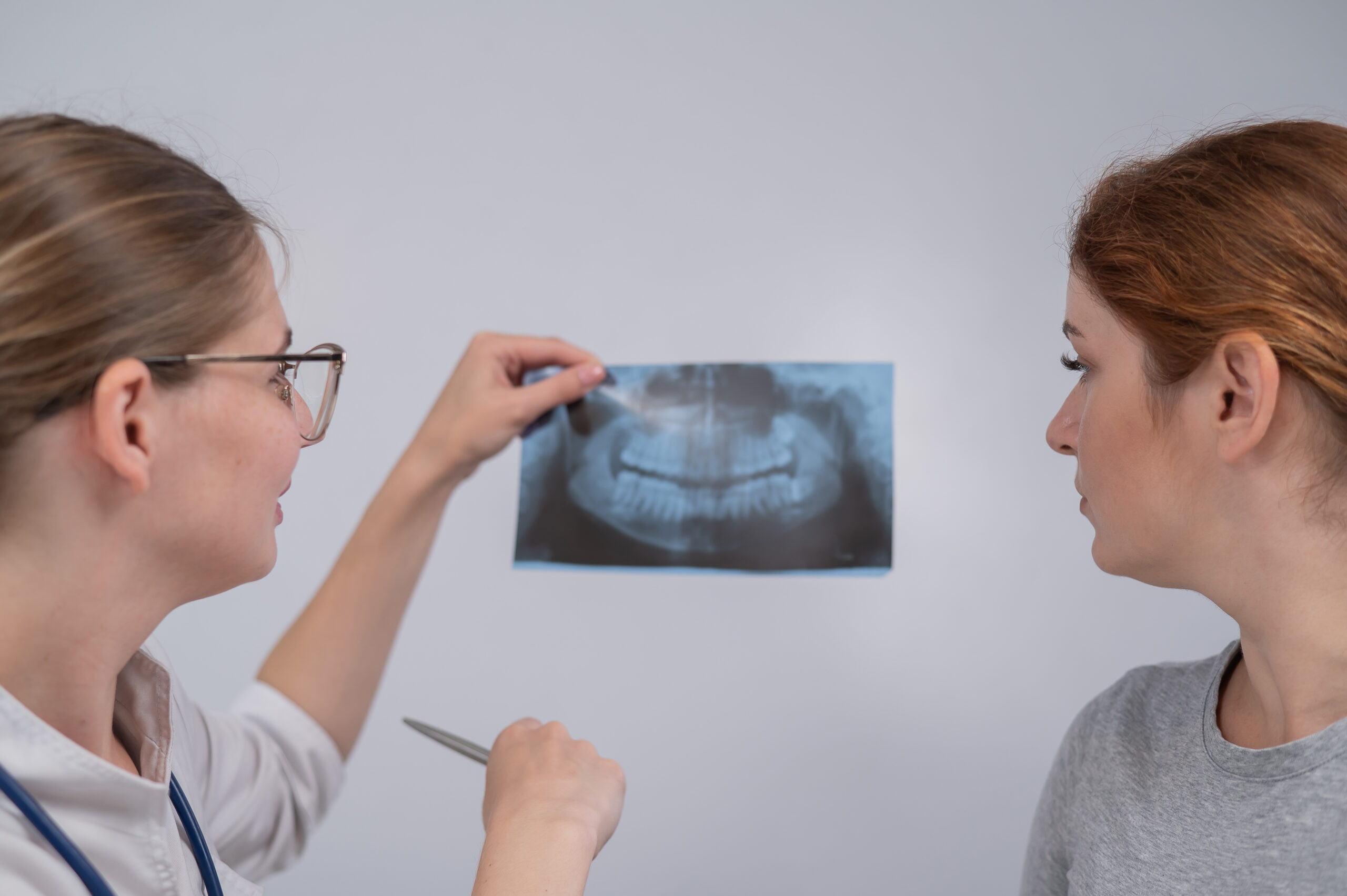 Wisdom teeth do not always need to be extracted
Wisdom teeth do not always need to be extracted
Reminding that 20-year-old teeth are the teeth in the back of our jaw, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Lect. Prof. Dr. Seda Altop said, “Because they are the last teeth to erupt, they often do not find a place in the jaw arch. In the 20s, diagnosis and, if necessary, intervention should be planned with a general evaluation after radiography. said.
Providing information on when wisdom teeth do not need to be extracted, Altop said, “Fully erupted wisdom teeth in the mouth; If it is in the occlusion, that is, if there is a tooth in return, it is in a proper position, does not damage the surrounding tissues and is healthy, there is no need for extraction.”
Bacteria danger in semi-impacted wisdom teeth
Talking about whether impacted or semi-impacted wisdom teeth require extraction or not, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Lect. Prof. Dr. Seda Altop, Üsküdar Dental Hospital said, “Gingivitis may develop due to bacterial accumulation between the gums and teeth in semi-impacted 20-year-old teeth in the jawbone. In this case, maxillofacial abscesses may cause facial swelling, pain, limitation in mouth opening and should be removed.”
Pointing out that wisdom teeth that are completely embedded in the jawbone can also cause problems, Altop concluded his words as follows, “Even if it is asymptomatic, the sac around it can turn into cysts in fully impacted wisdom teeth. Therefore, radiographic evaluation is required. The decision for extraction is made by evaluating the anatomical relationship with the nerve, whether a cyst is formed, and the damage to the surrounding tissues and teeth.”